Metal foam filter manufacturing process uses the web polyurethane foam as the carrier, makes the foam plastics evenly soaked to infiltrate the ceramic slurry, and then repeatedly squeezes the foam plastics to remove the excess slurry, so that the ceramic particles are fully removed. Evenly attached to the top of the foam plastic. Finally, it is dried and burned to a certain shape.
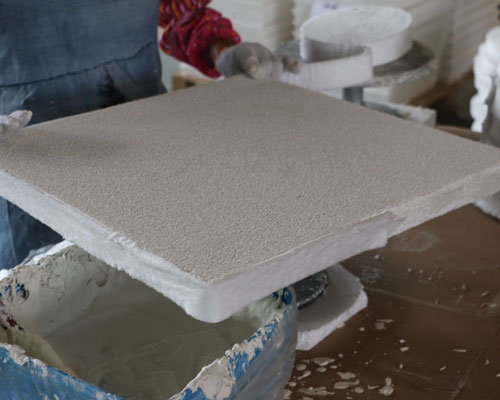

Foam properties directly affect the metal foam filter manufacturing process, and should have the following characteristics:
The mesh is uniform to ensure free penetration of the ceramic slurry and uniform coating.
Hydrophilic, can firmly adsorb the slurry.
It has enough elasticity and can quickly return to the original shape after extrusion.
It is volatile at medium temperature and below the firing temperature of ceramics, and will not pollute the ceramics.
Metal Foam Filter Manufacturing Process Influencing Factors
Ceramic foam slurry is made from refractory aggregate, sintering aids, adhesives, and other micro powders and water. The preparation of slurry is the key process. The ceramic slurry should have as high solid content as possible (slurry density is 1.8 ~ 22G / cm3, solid content is 50% ~ 65%), good thixotropy, and wettability. High solid content ensures that ceramic particles are attached to the foam screen to the greatest extent.
The thixotropy of ceramic filter strength is improved to promote the uniform formation of slurry and prevent clogging. If the wettability between the slurry and the ceramic foam is poor, the slurry will aggregate at the intersection of the foam structure, and the ridge will be less, and the strength will be reduced or even after the sintering.
The key to this process is the strength and uniformity of extrusion. If ceramic slurry remains in the foam, it will cause defects, such as smaller pore size or blockage. On the contrary, too little adhesion of ceramic paste will affect the strength of the product.
Green body drying period: the green body is dried at low temperature for a period of time to remove free water and obtain initial strength; in this stage, heating rate and temperature should be controlled to avoid deformation, slag, and cracks.
Foam evaporation time: at a certain speed, the heated object will be heated above the ignition point of the foam and heated for a period of time, so as to completely volatilize the foam. At this stage, the temperature rise is not too fast, otherwise it will reduce the intensity of the product and even cause waste.
Vitrification enters the stage of porcelain: heating to the sintering temperature at a faster speed and holding it for a period of time to fully sinter the green body. In this stage, the heating speed should not be too fast, otherwise, the front part of the porcelain will crack and collapse. After the product is fired, the cooling rate should not be too fast in order to prevent the filter from cracking.